Editor:
Prof. Dr. Christiane Zaborosch
Lecturer in Biochemistry
christiane.zaborosch@zhaw.ch
Introduction
In the development of new drugs, it is of interest in pharmaceutical research to determine the size of antibody-antigen complexes that have formed, since it is assumed that large complexes are cleared more quickly by the body, and thus the antigen is removed faster. Antibody-antigen complexes (mAb-Ag) can be analysed using MALDI-TOF-MS. However, non-covalent complexes are difficult to detect using MALDI-TOF-MS without sample preparation, as dissociation of the complex occurs during laser irradiation and co-crystallization with the matrix. In order to prevent dissociation during the MALDI process, chemical stabilization can be carried out by means of covalent cross-linking. For cross-linking of the antibodies with the antigen a homobifunctional, amine-reactive cross-linker BS(PEG)5 was employed (spacer: 21.7 Å). The crosslinker reacts with the free N-terminus and the ε-amino group of lysine side chains of the proteins. The nucleophilic N atom of the protein’s primary amine breaks down the carbonyl group of the cross-linker and an amide bond is formed by nucleophilic substitution. To analyse the major cross-linked protein complexes (> 150 kDa) with MALDI-TOF-MS, an HM1 high-mass ion conversion detector from CovalX was used.
Binding experiment with one mAb
To study the mAb-Ag complexes, a model system with IL-1β (Ag) and two anti-human IL-1β monoclonal antibodies XO01_γ2 and BS01 (mAb) was used. In the binding experiment XO01_γ2 or BS01 and IL-1β were mixed at the ratio of 1:2. The complexes formed from Ag and mAb were crosslinked through the addition of BS(PEG)5 in a 56-fold molar excess.
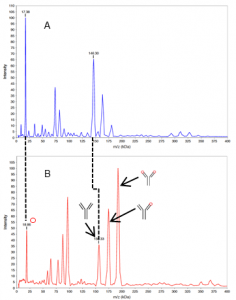
In the control spectrum (Fig. 1A) the peaks of the antigen IL-1β occurred at 17.4 kDa and those of the mAb XO01_γ2 at 146.3 kDa. The peaks at 163.3 kDa and 180.3 kDa corresponded to complexes without crosslinking. In the spectrum after crosslinking (Fig. 1B), two very high intensity peaks were observed at 163.4 kDa and 180.2 kDa, which could be attributed to the [XO01_γ2*1IL-1β] and [XO01_γ2*2IL-1β] complexes. The mass of the crosslinker was subtracted from the calculated masses of the complexes. BS01 was also crosslinked with IL-1β and analysed (data not shown).
Multi-binding experiment with two mAbs
In the multi-binding experiment larger mAb-Ag complexes were generated and the exact masses determined using MALDI-TOF MS. The two mAbs which are directed against different epitopes were mixed with IL-1β in a ratio of 1:2:1 (mAb1:Ag:mAb2) and then crosslinked with the crosslinker BS(PEG)5 in a 56-fold molar excess.
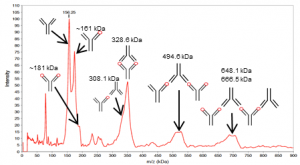
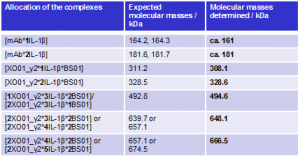
On the basis of the molecular masses, the peaks in the spectrum (Fig. 2) were attributed to the various mAb-Ag complexes (Tab. 1). Uncomplexed antigen was not detected; IL-1 β was therefore fully bound into complexes.
Conclusion
Using the crosslinker BS(PEG)5 the two mAbs XO01_γ2 and BS01 were covalently crosslinked with the antigen IL-1β and the resulting mAb-Ag-complexes were detected using MALDI-TOF-MS.
[ratings]
Thank you, Miriam, for your contribution. Have you ever tried to calculate the theoretical molecular mass of the antibody-antigen complexes? There’s an opportunity to consider multiple amino acid chains and custom defined modifications with Prot pi | Protein Tool.
Hi Roland,
Yes I calculated the theoretical molecular mass of the complexes that I expected. But it would be nice to recalculate the theoretical molecular mass with the Prot pi Protein Tool, to see what is the difference to my values.
Hi How to rule out Gas phase dimers and oligomers in MALDI MS spectra??
Hi Amit,
Before the binding experiments the antibodies and antigen were measured separately with MALDI-TOF-MS. We detected just small proportions of dimers and oligomers. Because of that, the formation of dimers and oligomers in the gas phase can be neglected.
Hi, is it possible to detect non-covalent complexes using MALDI-TOF-MS?
Hi pk service, non-covalent complexes are difficult to detect using MALDI-TOF-MS without sample preparation, as I described in my post. Dissociation of the complex occurs during laser irradiation and co-crystallization with the matrix. Anyway you can measure a small amount of the complexes but a sample preparation is in my opinion a must. To prevent dissociation during the MALDI process, you can stabilize chemicaly your non-covalent complexes by using covalent cross-linking. There exits a lot of different cross-linkers with different reactive sites and different spacer length. Depending of your non-covalent complex (caracteristics, distance antigen-antibody, …) you have to choose the… Read more »
Hi Miriam, really nice work! Could you please share some of your sample prep methods? I saw that you used Sinapinic acid as your matrix. What was the matrix reconstituted with and did you premix the matrix with your sample prior to deposition on the plate?
Hi Elsa, Thank you very much. I used Sinapinic acid (SA) matrix for MALDI-MS (from Sigma), 10 mg/ml in water/acetonitrile (ACN, Sigma)/trifluoroacetic acid (TFA, Sigma) (ratio 1:0.5:0.001). The proteins were diluted with water to a concentration of 2 mM. The reduced an reduced deglycosylated antibody samples were measured undiluted (0.1 mg/ml, appr. 1.37 mM). For the measurements 1 ml of the diluted protein sample was mixed with 1 ml matix (1:1). Of this mix were pipetted two times 1 ml on the sample plate (MTP 384 ground steel, Bruker Daltonics) and dried at room temperature (Dried Droplet method). After the… Read more »