The isoelectric point (pI) of native (not denaturated) proteins is important in several separation techniques. The pI is defined as the pH value at which the positive and negative charges on the protein are balanced and the net charge is zero. To determine the pH at which the net charge is zero, the charge on the protein is calculated at multiple pH values using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, as described by Sillero and Ribeiro (1989).
Charge of type N (negative) groups:
Charge of type P (positive) groups:
Total charge:
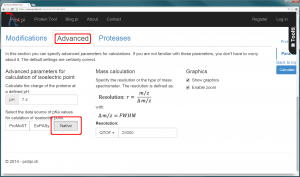
The usage of appropiate pK values is of crucial importance to caluclate correct pI. For denatured proteins, Bjellqvist et al. (1993) published an accurate methode to predict the focusing position of polypeptide in immmobilized pH gradients under denaturing conditions (8 M urea). On the other hand, amino acid side chain pK values of native proteins where measured using NMR. Grimsley et al. (2008) summarized 541 pK values of 78 folded proteins measured with NMR which were taken to calculate average pK values for each type of amino acid side chain. An algorithm to determine the isoelectric point of native protein using these average pK values is implemented in Prot pi’s Protein Tool. Choose “native” option in the “Advanced” tab to take advantage of this algorithm (figure 1).
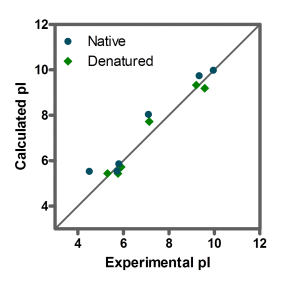
The calculated and the measured isoelectric point of five proteins with different properties were compared. Homo-and heteromultimeric, basic and acidic as well as small and very large proteins were taken to validate the calculated pI (table 1).
Table 1: Calculated pI compared with measured pI out of literature of native and denaturated proteins. Measured pI were taken from Ui (2006), except: *) Przybylski (2015) and **) Stone-Wolff (1984)| Protein | Uniprot # | pI, measured, native | pI, measured, denaturated | pI, calculated, native | pI, calculated, denatured | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interferon-γ | >sp|P01579|24-161 | 9.95* | 9.2** | 9.985 | 9.329 | Homodimer |
| Hemoglobin | >sp|P69905|2-142 >sp|P68871|2-147 | 7.1 | 7.14 | 8.037 | 7.721 | Heterotetramer |
| Insulin | >sp|P01317|85-105 >sp|P01317|25-54 | 5.72 | 5.76 | 5.535 | 5.438 | Disulfide linked heterodimer |
| Ribonuclease | >sp|P61823|27-150 | 9.33 | 9.58 | 9.743 | 9.19 | Basic pI |
| Thyroglobulin | >tr|D1KKB3|20-2692 | 4.5 | 5.3 | 5.534 | 5.433 | Very large (582.5 kDa) |
| Serum albumin | >sp|P02768|25-609 | 5.8 | 5.9 | 5.861 | 5.724 | Acidic pI |
The calculated pI values showed reasonably good agreement with experimental ones for all of the six proteins under native and denaturing conditions over a wide range of physico-chemical properties (figure 2).
Conclusion
Prot pi provides an accurate tool to calculate isoelectric points of denatured and native proteins that takes charge contributions of multiple subunits, disulfide bonds and posttranslational modifications into account.
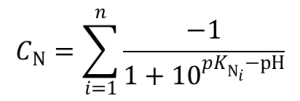
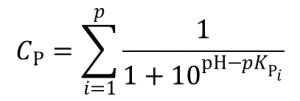
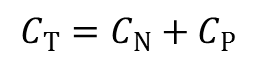
I Don’t know if my computer is glitching, but your profile picture is on top of “Author’s name”.
Thanks for reporting this! The issue was caused by an outdated setting, which is now fixed.
Hello, how good night, in which menu can I know the isoelectric point of my denatured protein and which parameter to take from my isoelectric point the first without placing the native option or should I select native?
Dear Reguinaldo
For denatured proteins it is best to use the “ProMoST” option, which is the standard.
Hello, the isoelectric point of my protein was different in prediction with ProMost, Expasy and Native. Which one should I used.
If you are not sure which algorithm to use, you are certainly well advised to use ProMoST. It usually provides the most accurate results.
Hey, what is the unit of the net surface charge z at a given pH?
The charge z (actually the charge number) has no unit. Multiply the charge (number) z by the elementary charge (e) to get the absolute value of charge (q) of a ion with the unit eV.
Hi, can you please comment on the best way to use these tools for antibody heavy / light chains and how the calculation is performed across the chains? Do you average them or something more complicated?
Use a subunit for each chain. This is important for the correct calculation of the mass and pI.